The international patient department, which is called IPD , is a unit in the hospital that serves international patients in order to coordinate the provision of medical services.

Madaran Hospital has established a separate department called International Patient Department (IPD) for international patients and their well-being during hospitalization.
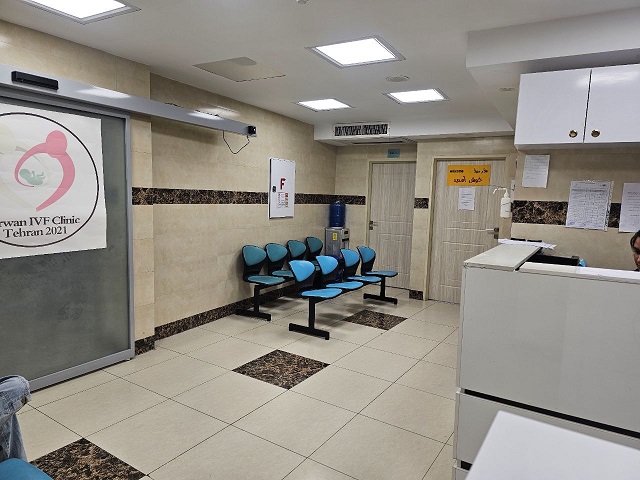



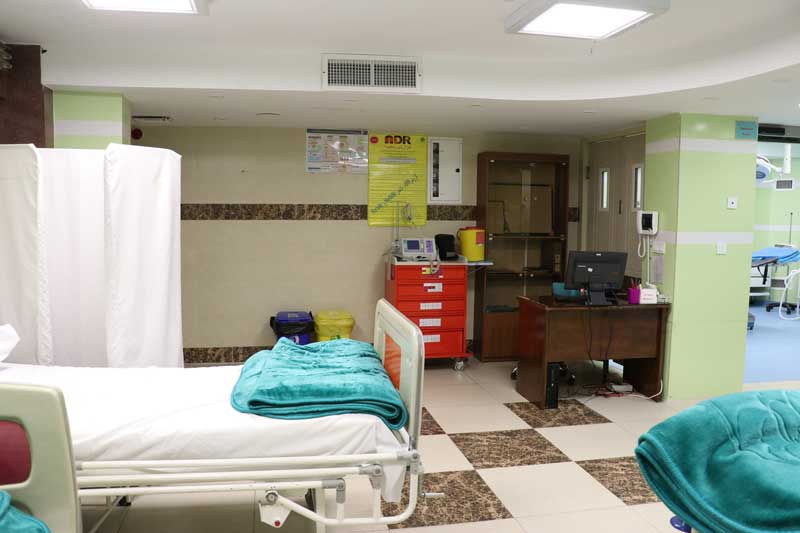
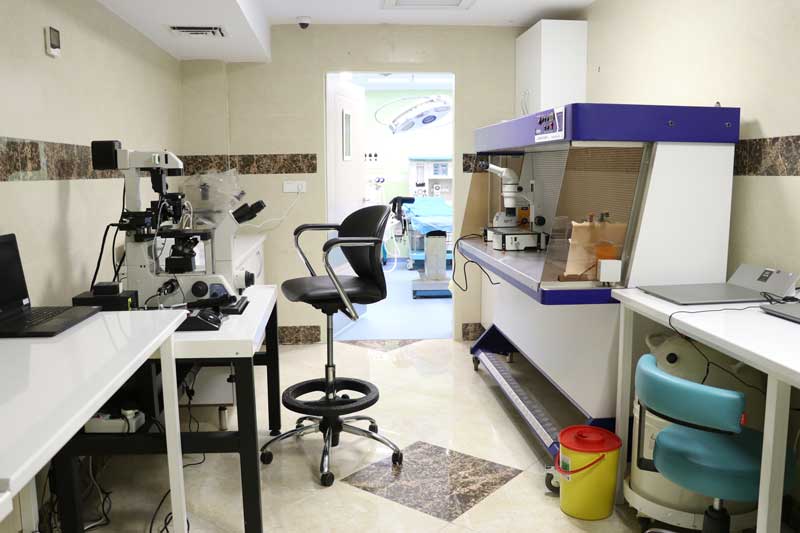
Sirvan IVF Clinic is located on the fifth floor of Madaran Hospital and is ready to serve dear people with the establishment of infertility clinic and andrology laboratory.
This center has a staff consisting of gynecologists with infertility fellowship, urologist, reproductive health and sexual health and an experienced embryology team.
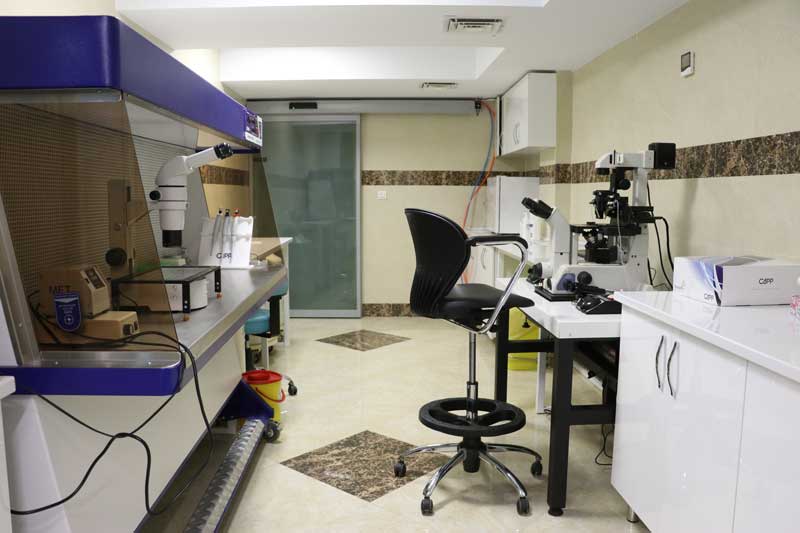

Services of the IVF clinic of Madaran Hospital
Infertility treatment
IUI intrauterine insemination
Microinjection IVF
Fertility preservation
Fertility services
Pregnancy and women’s health services
Diagnostic and treatment services for recurrent miscarriage
Specialized services for men
Men’s specialized surgeries
PSG and PGD sex determination
Embryo hatching
Donated eggs and embryos
Freezing testicular and ovarian tissue
Embryo, egg and sperm freezing
laparoscopy
hysteroscopy
Reproductive health and sexual health counseling

